We use cookies to make your experience better. To comply with the new e-Privacy directive, we need to ask for your consent to set the cookies Learn more.
A recirculating system is a unique design that provides water savings in either a chemical-free system or in a system that uses residual disinfectants. Recirculation provides continuous water flow in an effort to keep animal drinking water from becoming stagnant. The concept is simple – water is pumped from a storage tank, through an ultraviolet (UV) disinfection unit, to the room distribution system,
and back to the storage tank. Therefore, water is never wasted.
ADVANTAGES OF A BALANCED RECIRCULATING SYSTEM:
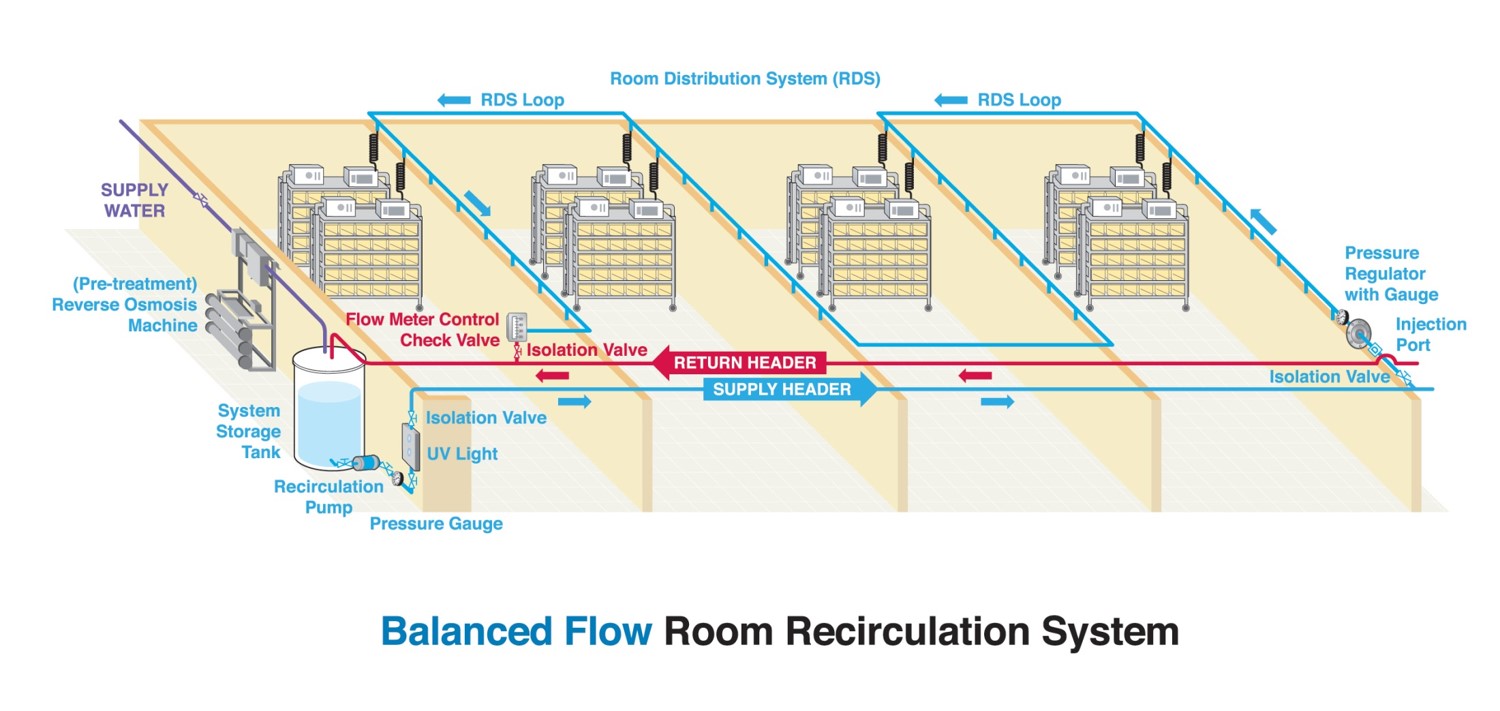
Header – Room Distribution System Recirculation
In this type of system, water is recirculated through the header and room distribution system (RDS), but not through the rack manifolds. Water is pumped from the storage tank, through the UV unit, and through the supply header at high pressure. Each room distribution loop then feeds off of the supply header at a controlled, reduced pressure. Water exits the RDS loop and goes back to the storage tank through the return header.
A facility using this design may choose to incorporate an On-Line Rack Flush system as well. This will guarantee a fresh supply of water into the racks, by periodically draining the water in the manifolds.
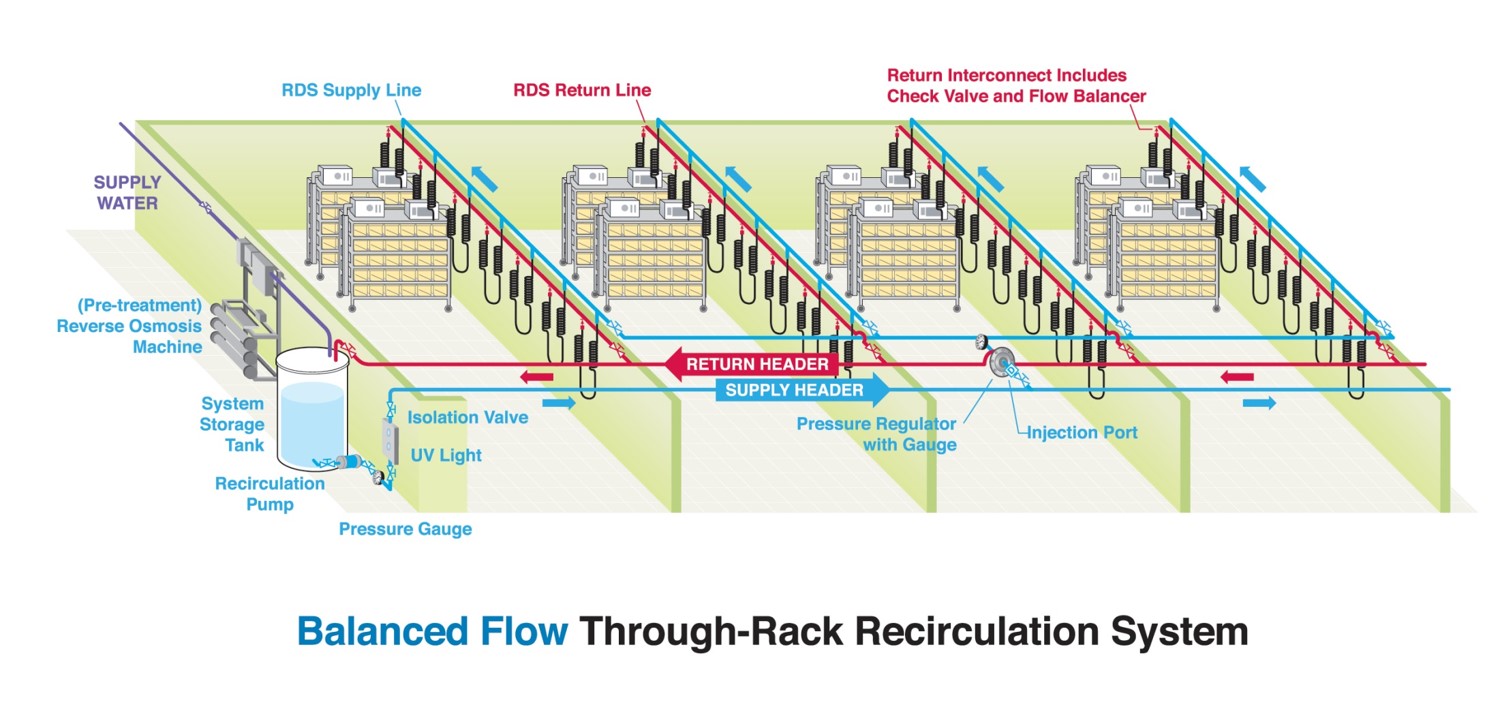
Through the Rack Recirculation
In a rack recirculation system, the water is recirculated similar to the header room distribution system, except the water also enters the rack manifolds, bringing fresh water to each animal drinking valve. This is particularly important for species such as mice, that consume small amounts of water.
Water is pumped from the storage tank, through the UV unit, and through the supply header at high pressure. Each room distribution loop feeds off of the supply header at a controlled, reduced pressure. Water is distributed evenly through the racks from the RDS supply line. The water exits the RDS return line and goes back to the storage tank through the return header.